Mitigating the Devastation: Addressing Flood Risks in Pakistan
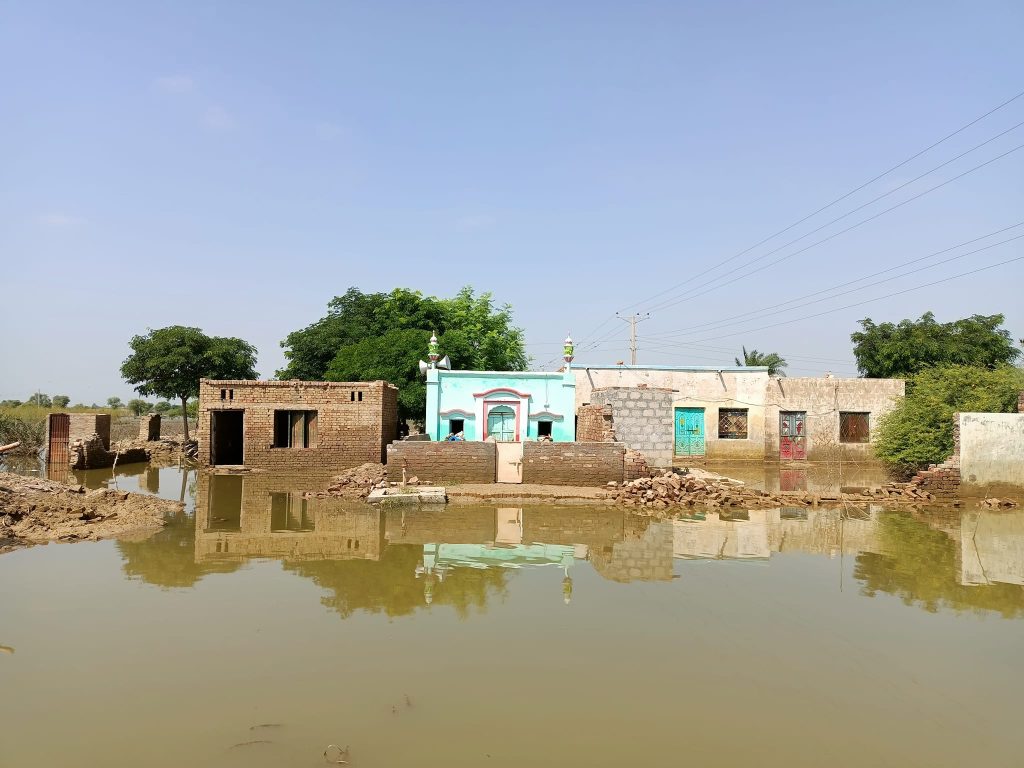

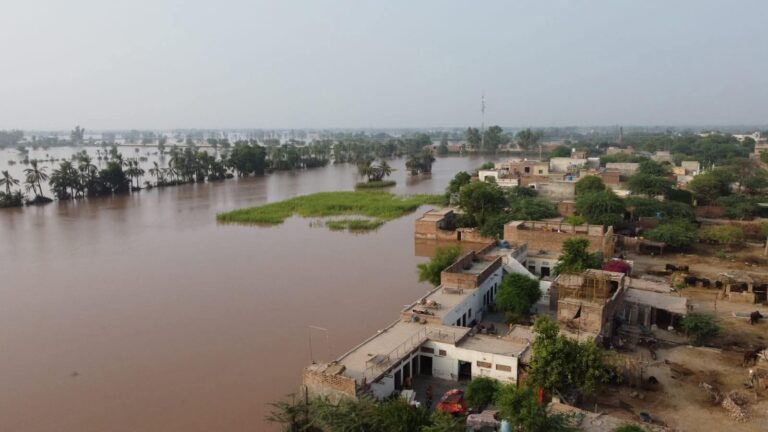
Floods, while a natural phenomenon, can wreak havoc when they occur in excess, turning a vital resource into a force of destruction. Floodwaters can displace communities, destroy both rural and urban areas, and alter the landscape permanently. The adage “too much of anything is bad” holds true, as excessive rainfall and subsequent flooding transform nature’s blessing into a catastrophe. The increasing intensity and frequency of rainfall, exacerbated by climate change, has heightened the flood risk, as evidenced by the devastating floods that struck Pakistan two years ago, affecting nearly one-third of the country.
Key Questions Surrounding Floods
– Why is there an increase in rainfall?
– What causes water to turn into a flood?
– Why do floodwaters cause severe damage in certain areas?
– What are the solutions to mitigate flood damage?
In today’s scientific age, answering these questions is relatively straight forward; though implementing ground-level solutions remains challenging, but not impossible. The rapidly growing global population, particularly in developing countries, is at the root of many environmental issues. Humans, in their quest to adapt the planet to their needs, have altered the natural environment significantly. Deforestation, urbanization, the construction of roads and factories, and the use of various modes of transport all contribute to environmental degradation. These activities have led to a rise in global temperatures, increased carbon emissions, and consequently, the melting of glaciers, more intense monsoons, and rising sea levels. When natural or artificial barriers obstruct water flow, the accumulated water can cause extensive damage, transforming into uncontrollable floods.
Human Factors Contributing to Flood Disasters
Human activities, particularly the construction of artificial dams and the encroachment on riverbanks, play a significant role in exacerbating flood conditions. The recent catastrophic flooding in Pakistan can be attributed to several factors, including the failure to construct necessary dams, illegal encroachments on river crossings, poor planning and execution of infrastructure projects, and rampant corruption. These issues, coupled with the effects of climate change and global warming, have created a perfect storm, making Pakistan highly vulnerable to flood disasters.
Detailed Causes of Flood Situations in Pakistan
1. The current floods in Pakistan are primarily caused by the rapid melting of glaciers, heavy monsoon rains, and cloudbursts in mountainous regions. Historically, such events occurred infrequently, but climate change has made them more common and severe. Provincial governments must be prepared to handle these situations effectively.
2. Unauthorized construction on riverbanks obstructs water flow, leading to flood situations. Despite existing laws to protect rivers, encroachments continue, particularly in regions like Azad Kashmir, Baltistan, and Khyber Pakhtunkhwa. These illegal structures increase the risk of financial and human losses during floods. It is crucial for the government to take timely action to remove such encroachments and prevent future violations.
3. Settling and farming on old riverbeds, which can still carry water during floods, exacerbate flood damage. Such activities obstruct the natural flow of water, increasing flood intensity. Government intervention is necessary to prevent settlements in these areas and allow old river channels to help dissipate floodwaters.
4. Roads and canals constructed without proper bridges over natural waterways can worsen flood conditions. The absence of proper drainage systems causes water to accumulate, damaging fertile lands and turning them into lakes. This issue is particularly prevalent in Sindh, where the lack of proper infrastructure planning has contributed to widespread devastation.
5. Poor maintenance and illegal encroachments on sewer systems worsen flood situations. Blocked sewers prevent water from draining properly, causing floods to spread over large areas. Regular cleaning and maintenance of sewer systems, especially in urban areas, are crucial to prevent such disasters.
6. The lack of forests in flood-prone areas contributes to soil erosion and weakens natural barriers against floods. Planting trees along canals, rivers, and embankments can strengthen these areas and reduce flood damage. The government must prioritize reforestation efforts to mitigate future flood risks.
7. Building in low-lying floodplains without considering historical practices has led to increased flood damage. In Sindh, many communities were severely affected because they were situated in areas prone to flooding. A strategic approach to resettlement in flood-prone areas is essential to avoid similar disasters in the future.
Lessons from the Recent Floods
The recent floods in Pakistan have caused widespread devastation, displacing millions, causing numerous deaths, destroying homes, killing livestock, and washing away infrastructure. The estimated economic loss exceeds thirty billion dollars. It is imperative for future governments to learn from this disaster and take proactive measures. These include increasing forest cover, timely maintenance of canals and embankments, improving flood forecasting systems, eliminating illegal riverbank encroachments, and constructing dams at suitable locations. By addressing these issues, Pakistan can significantly reduce the impact of future floods. Implementing a comprehensive strategy that includes reforestation, infrastructure improvements, and better flood forecasting will help protect the country from the devastating effects of climate change-induced floods.